Uncertainty篇(二),用隐式马尔可夫链解遗传问题 | Word count: 1.3k | Reading time: 5min | Post View:
前言 完整代码见 https://github.com/zong4/AILearning。
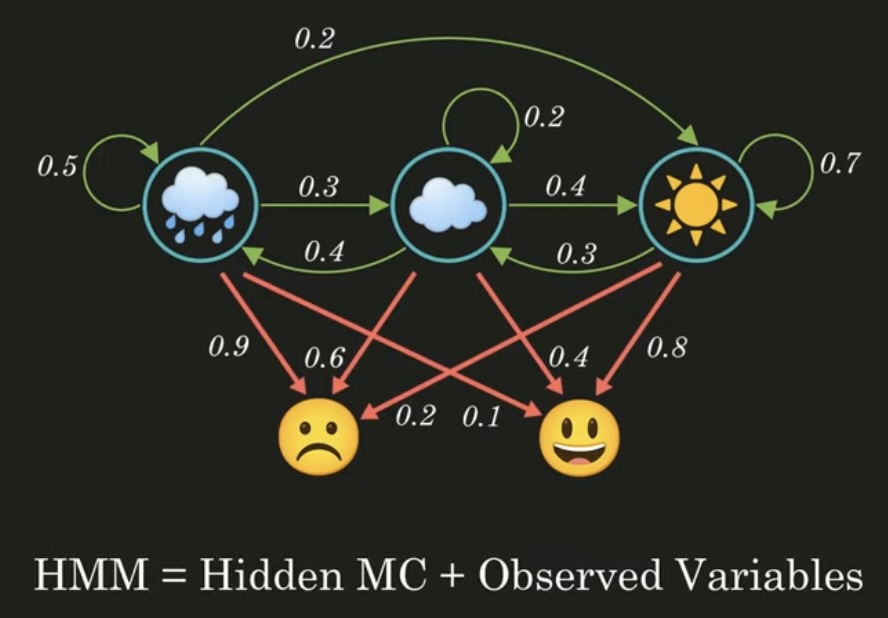
隐式马尔可夫链 隐式马尔可夫链就是在马尔可夫链的基础上多了观察变量,如下图上半部分就是我们上一篇讲的马尔可夫链,具体可以阅读这一篇 。
OK,那除此之外,在显式马尔可夫链中,我们是知道整个转移模型的(也就是上图的绿线),而在隐式马尔可夫链中我们只知道转移模型中的各状态对应传感器状态(也就是观察变量)的概率(也就是上图的红线)。
那自然我们除了之前的转移矩阵还有一个新的矩阵如下图所示。
于是我们就可以去计算各种情况的发生概率了。
不过大部分情况,我们之所以要用隐式马尔可夫链是因为我们不知道显式的马尔可夫链 ,比如下图的问题,对于这样的 笑脸 -> 笑脸 -> 苦脸 的顺序,天气的顺序最有可能是怎么样的?概率又是多少呢?
具体的计算思路就是类似于有记忆的递归算法 ,如下哦,这就不多说了吧,毕竟概率也是左加右嘛。
遗传问题 OK,接下来就让我们来试着解一下遗传问题。
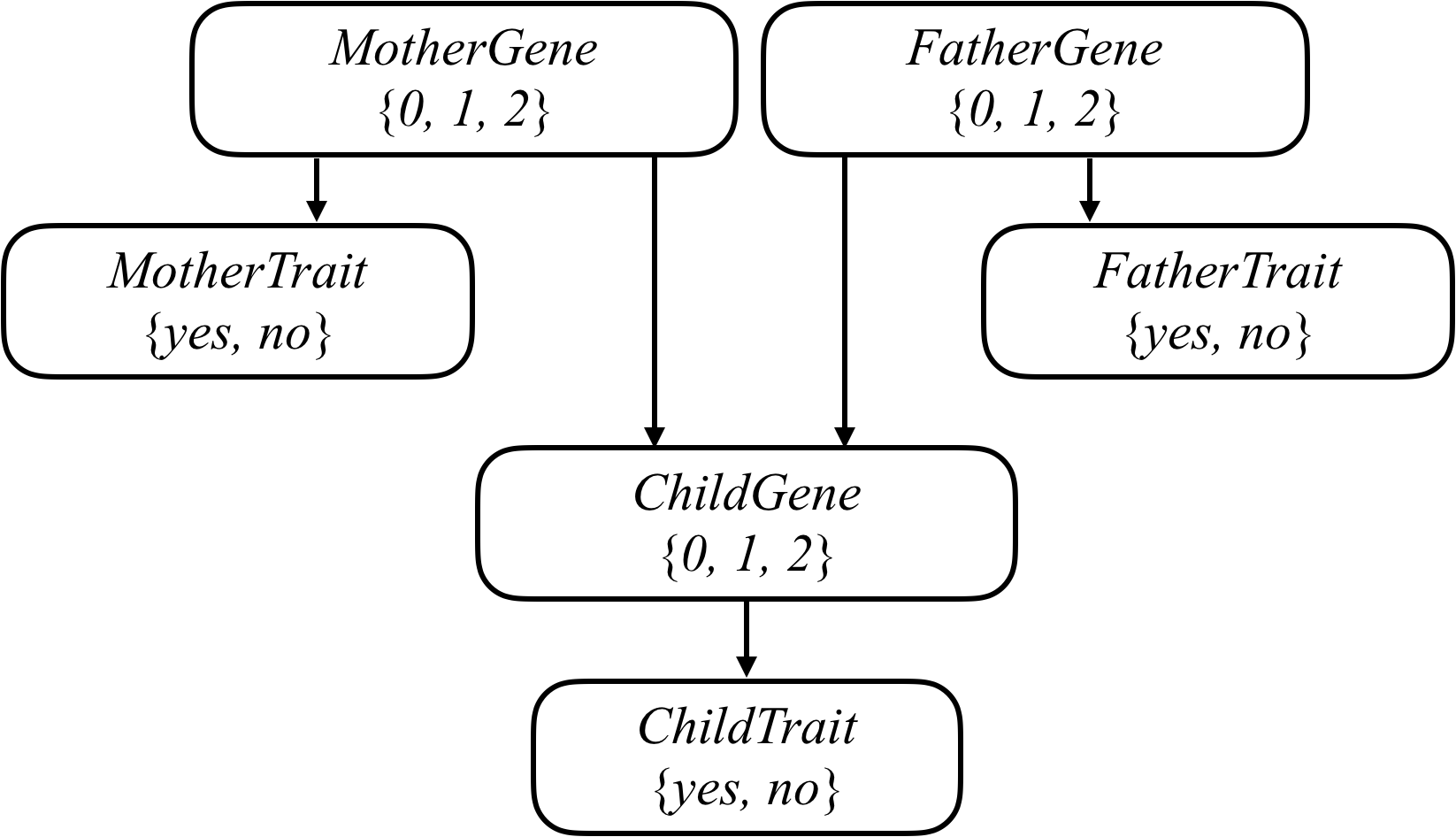
我们可以将任何遗传问题用下图表示。
超参数
来吧,首先是人群中(独立)携带指定基因的概率,用来算一开始第一步的概率,相当于初始状态。
然后是携带基因的表现概率,就是说有的人携带了也不会表达出来,表达出来了才算基因起作用了。
最后是突变概率。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 PROBS = { "gene" : { 2 : 0.01 , 1 : 0.03 , 0 : 0.96 }, "trait" : { 2 : { True : 0.65 , False : 0.35 }, 1 : { True : 0.56 , False : 0.44 }, 0 : { True : 0.01 , False : 0.99 } }, "mutation" : 0.01 }
代码逻辑 这里的计算方法是考虑每一种情况然后累加概率,可以通过以下函数计算任一种情况的概率。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 def joint_probability (people, one_gene, two_genes, have_trait ): """ Compute and return a joint probability. The probability returned should be the probability that * everyone in set `one_gene` has one copy of the gene, and * everyone in set `two_genes` has two copies of the gene, and * everyone not in `one_gene` or `two_gene` does not have the gene, and * everyone in set `have_trait` has the trait, and * everyone not in set` have_trait` does not have the trait. """ p = 1 for person in people: genes = 2 if person in two_genes else 1 if person in one_gene else 0 trait = person in have_trait mother = people[person]["mother" ] father = people[person]["father" ] if mother is None and father is None : p_gene = PROBS["gene" ][genes] else : n_genes_mother = 2 if mother in two_genes else 1 if mother in one_gene else 0 n_genes_father = 2 if father in two_genes else 1 if father in one_gene else 0 if genes == 0 : if n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 0 : p_gene = (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) elif (n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 1 ) or (n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 0 ): p_gene = (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) * 0.5 elif n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 1 : p_gene = 0.5 * 0.5 elif (n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 2 ) or (n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 0 ): p_gene = (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) * PROBS["mutation" ] elif (n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 2 ) or (n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 1 ): p_gene = 0.5 * PROBS["mutation" ] elif n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 2 : p_gene = PROBS["mutation" ] * PROBS["mutation" ] elif genes == 1 : if n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 0 : p_gene = (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) * PROBS["mutation" ] + PROBS["mutation" ] * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) elif (n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 1 ) or (n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 0 ): p_gene = 0.5 * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) + 0.5 * PROBS["mutation" ] elif n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 1 : p_gene = 0.5 * 0.5 + 0.5 * 0.5 elif (n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 2 ) or (n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 0 ): p_gene = (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) * PROBS["mutation" ] + PROBS["mutation" ] * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) elif (n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 2 ) or (n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 1 ): p_gene = 0.5 * PROBS["mutation" ] + 0.5 * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) elif n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 2 : p_gene = PROBS["mutation" ] * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) + (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) * PROBS["mutation" ] elif genes == 2 : if n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 0 : p_gene = PROBS["mutation" ] * PROBS["mutation" ] elif (n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 1 ) or (n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 0 ): p_gene = 0.5 * PROBS["mutation" ] elif n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 1 : p_gene = 0.5 * 0.5 elif (n_genes_mother == 0 and n_genes_father == 2 ) or (n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 0 ): p_gene = PROBS["mutation" ] * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) elif (n_genes_mother == 1 and n_genes_father == 2 ) or (n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 1 ): p_gene = 0.5 * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) elif n_genes_mother == 2 and n_genes_father == 2 : p_gene = (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) * (1 - PROBS["mutation" ]) p_trait = PROBS["trait" ][genes][trait] p *= p_gene * p_trait return p
在任一情况下,one_gene 包含所有只携带一个基因的人,two_genes 则包含所有只携带两个基因的人, have_trait 包含所有有症状显示的人。
通过遍历所有人,计算他们满足该情况的概率后累乘,即为这种情况出现的概率。
后记 感觉这种方法好麻烦,而且我算那段基因概率的时候头好大,感觉好不确定,还是用递归来做吧,应该会简单。